The cannabis plant contains over 500 known compounds, including over a hundred different cannabinoids and terpenes. Cannabis first starts as a flower. The raw flower can be processed into different products that affect its onset of action and total duration of effects. There are over 100 discovered cannabis derived cannabinoids that are concentrated within the female plant.
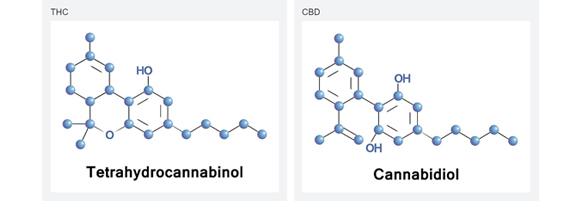
The most abundant cannabinoids are CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), which constitute the majority of physiologically active and/or psychoactive molecules found in cannabis.
Cannabinoids impact the body’s physiological functions through a cellular signaling pathway known as the Endocannabinoid System (ECS). This system affects many biological processes, including metabolism, appetite, pain, sleep, mood, learning and memory, cardiovascular function, gastrointestinal function, the immune system, and neural development.
The rest of the ingredients found in cannabis are made up of terpenes, phenols, and flavonoids. These diverse classes of chemical compounds are said to lead to physiological changes in the body.
Hemp is a variety of cannabis that has low to no THC and a high level of CBD. Hemp related products, such as hemp oil and hemp-extracted CBD oil, have high levels of CBD and low to no THC.
There are three different varieties of the cannabis plant that have been cultivated around the globe: Sativa, Indica and Ruderalis. However, given cross-breeding over the years, the vast majority of strains are now hybrids. C. sativa and C. indica are the two primary subspecies from which most commercial cannabis strains are derived. These subspecies tend to produce contrasting effects because sativa is enriched for THC whereas indica is enriched for CBD. The range of THC:CBD ratios are derived from sativa-indica hybrid strains.
Cannabis Compounds
The Cannabinoids
THC, which is the primary psychoactive cannabinoid synthesized by cannabis, has clinical properties that include analgesia, nausea suppression, muscle relaxant activity, and appetite stimulation. Although not entirely free of side-effects, CBD, which is a major non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in cannabis, has numerous medicinal properties including anti-psychotic and anxiolytic activities; anti-inflammatory activity; and anti-convulsive/anti-seizure activity.
Terpenes
Each individual terpene is associated with unique effects. There have been approximately 100 terpenes identified so far. Often called the aromatic oils of cannabis, terpenes give each cannabis strain their distinctive colour, characteristic fragrance and taste of the plant. Some terpenes promote relaxation and stress-relief, while others promote focus and acuity.
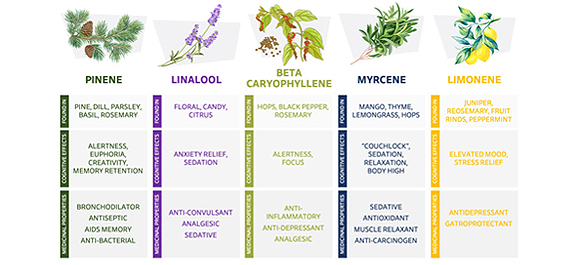
Different strains of cannabinoids and terpenes are effective at treating different conditions. A cannabis product that is optimal for one individual may not be suitable for another person because of variables including genetics and individual medical conditions. Reducing trial and error side effects from the use and prescribing of cannabis can occur by knowing your drug metabolism tendencies toward THC and CBD. Completing such a pharmacogenetics test will not only provide you and your prescriber this valuable knowledge but also inform you as to how cannabis will interact with other drugs that you consume, including alcohol and caffeine. Genetics testing can also offer insights about cannabis efficacy toward certain health conditions.



